Class Reference
This class reference is incomplete. You can help complete it by making an issue on GitHub or contributing to the class reference directly.
Trenchbroom Settings
These classes enable various Trenchbroom features for use in your game.
TrenchbroomTag
A matching filter that identifies type of brushes and textures and applies in-editor appearance. Does not affect in-game appearance or in-game functionality.
Tag Name
Name to describe this tag. Not used as the matching pattern.
Tag Attributes
An array of strings determining the in-editor appearance of brushes/faces that match this tag.
Current available attributes:
_transparentmakes the face semi-transparent
Tag Match Type
Detemines how the tag is matched.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
TEXTURE | Tag applies to any face with a texture matching the texture name. |
CONTENT_FLAG | Tag applies to any brush with a content flag matching the tag pattern. |
SURFACE_FLAG | Tag applies to any face with a surface flag matching the tag pattern. |
SURFACE_PARAM | Tag applies to any face with a special surface param. See Trenchbroom Manual for more info. |
CLASSNAME | Tag applies to any brush entity with a class name matching the tag pattern. |
Tag Pattern
A string that filters the specific flag, param, or classname to use. * can be used as a wildcard to include multiple options.
Example: trigger_* for the Classname match type will apply to all brush entities with the trigger_ prefix.
Texture Name
A string that filters the specific texture to apply this tag with. Only applies for the Texture tag match type.
QodotTrenchbroomConfig
Export File
Creates a new subfolder in the Trenchbroom games folder, named after your Game Name. It also adds (or updates) files to the subfolder: A GameConfig.cfg file, an Icon.png, and all FGDs linked in the Fgd Files array.
Trenchbroom Games Folder
The system location of your Trenchbroom games folder. This is either found inside your Trenchbroom installation, or your user folder. See Config Folder Propeties for common locations on various OSes.
Game Name
Unique identifier for your project in Trenchbroom’s “select game” folder. Game names can contain spaces.
Icon
Pulls from your project’s res://icon.png file by default.
Fgd Files
A list of all FGD files to include in the Game Definition.
Brush Tags
A lookup pattern for all brush entity classnames in the map to apply editor hints, such as _transparent. Only affects appearance in Trenchbroom, does not apply to making materials transparent in Godot.
Face Tags
A lookup pattern for all texture names in the map to apply editor hints, such as _transparent. Only affects appearance in Trenchbroom, does not apply to making materials transparent in Godot.
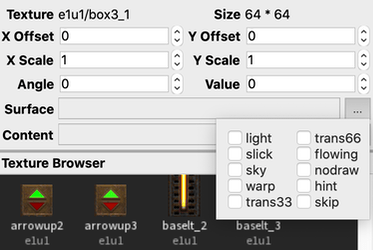
Face Attrib Surface Flag
Creates a map-wide boolean that can be applied to any face in Trenchbroom’s face editor. Surface flags mark a face with a specific property, usually for rendering purposes.
Quake 2 uses these for visual effects like “light”, “warp”, “moving”, “nodraw”, “sky”, and more. Read more about Face Attributes in the Trenchbroom Manual.
Face Attrib Content Flag
Creates a map-wide boolean that can be applied to any face in the face editor. Content flags mark a brush with a specific property, usually for gameplay.
Quake 2 uses these for gameplay elements like “playerclip”, “monsterclip”, “water”, “lava”, “slime”, “mist”, and more. Read more about Face Attributes in the Trenchbroom Manual.
Trenchbroom and Qodot Shared
These entities are read between both Trenchbroom and Qodot to represent the same core data.
QodotFGDFile
Fgd Name
Reserves a namespace for your entity definitions in Trenchbroom under this name.
Note
Trenchbroom will throw an error if you use two FGDs with the same Fgd Name. If you have Qodot.fgd as a base, make sure to change your own Fgd Name to something else.
Entity Definitions
An array containing Entity Definition resources.
Note
Trenchbroom will fail to load any entity definitions missing a classname.
QodotFGDClass
Classname - The name for this class in Trenchbroom. Cannot contain spaces.
Description - A short description that displays in Trenchbroom’s entity browser when this entity is selected.
Qodot Internal - Hides the entity in Trenchbroom’s entity browser.
Qodot can still refer to this entity for building other entities (like base entities). Base Entities are already hidden in Trenchbroom by default, in most cases you can leave this off.
Base Classes - An array of template entities to inherit properties from.
All base classes placed here will give the same class properties, meta properties, and property descriptions to the current entity definition.
Class Properties - A dictionary of properties.
Keys must be of type String. Keys are read as the property name in Trenchbroom.
Values must be of the following types:
Once exported to the Trenchbroom game config, the dictionary values are written by editing entities in Trenchbroom, and read by accessing properties on a QodotEntity once the map is built.
You can also set default values for your properties by repeating this process in Meta Properties, matching the key names and value datatypes from this dictionary.
Class Property Descriptions - A dictionary of descriptions for each property, visible in Trenchbroom.
Ensure the description’s key matches the property’s key. Description values can only be strings.
Meta Properties - Editor-specific properties, such as the default color and size used to represent this class. Primarily used by point classes.
Keys must be of type String. Values must be a type determined by the key name.
Possible key/value pairs include: | Key String | Value type | | ———- | ———- | | size | AABB | | color | Color | | model | Dictionary |
Flexible (assimp) model support in Trenchbroom is new as of Trenchbroom 2022.2. Documentation for using Qodot with the new model system is still in progress. Read Displaying Models for Entities for more information on model support and Trenchbroom’s expression language.
Node Class - The type of Godot node to spawn at this location.
Transient Node - Determines if QodotMap calls queue_free() on this node when the map finishes buliding. Removing transient nodes is the last post attach step when building a map. Transient nodes are not given priority over other entities during the build.
This value should stay unchecked unless it is desirable to remove this node after building the map.
QodotFGDPointClass
A single point for an entity.
Scene File - The .tscn Godot scene that spawns in place of QodotEntity. The easiest way to spawn a specific node at a specific point.
Scene File takes priority over every other option here, especially if there’s already a script attached to the .tscn file.
Script Class - The script to attach to your entity’s root node. See Scripting Entities for details.
Node Class - The type of node to spawn at this location. This property should match the extends of your Script Class. You can ignore this property if you’re using a Scene File.
With those properties covered, there’s a few tricks you can use to get more specific results.
If you want to create an RigidBody node without a .tscn using a point entity, extending RigidBody in thes script prevents you from accessing the class property values set in Trenchbroom. However, extending QodotEntity prevents you from accessing the functions and signals of a RigidBody.
You can get around this by extending QodotEntity and using var body = RigidBody.new() and add_child(body) to add more complex nodes as children, while still having access to the properties dictionary. This can be repeated for other children like MeshInstance and CollisionShape.
QodotFGDSolidClass
Solid classes can have multiple brushes (select multiple brushes before creating the entity). These properties apply to the solid class as a single node, with each brush built as one CollisionShape child.
Spawn Type - Changes how the QodotMap arranges these brushes in its node hierarchy.
There are 4 settings:
- Worldspawn
- Merge Worldspawn
- Entity
- Group
Worldspawn contributes this entity’s brushes to a primary StaticBody node. Intended for the Worldspawn definition only.
Worldspawn contributes this entity’s brushes to a primary StaticBody node without overriding the original definition of Worldspawn.
Group separates brushes into a new StaticBody node. Intended for grouped brushes.
Entity separates brushes into a node separate from the primary StaticBody, supporting scripts and CollisionObject node types.
Build Visuals - Builds a MeshInstance child for the solid class when checked. Does not build a MeshInstance child when unchecked.
Node Class - Sets the node type of the solid class root. If you’re adding a Script Class, this value should match the extends of the script. See Scripting Entities.
Collision Shape Type - Changes the type of CollisionShape resource used for CollisionShape children.
- None
- Convex
- Concave
Script Class - The script applied to the entity’s node when built.
Class Property Data Types
You can define properties for entities in the Class Properties dictionary. The “key” for each dictionary entry should be a String. The “value” can only be one of these 8 data types:
- Bool
- Int
- Float
- String
- Vector3
- Stored as a string in the form X Y Z
- Color
- Stored as a string in the form R G B
- Dictionary
- Used for defining a set of choice key strings and their associated values
- Will display a dropdown in compatible editors
- Available Dictionary value types haven’t been thoroughly tested
- Array
- Used for bitmask flag properties
- Will display a grid of checkboxes in Trenchbroom
- Used in Quake to indicate which entities spawn on different difficulties - easy, medium, hard
- Each entry in the array should be an array, with three elements:
[name: String, value: bool/float/int/String, default: same type as value]
Note on Arrays
Arrays create flags. When you add an Array as a class property, it must contain other Arrays, each Array creating one flag. These flag Arrays must have 3 items: Name, Value, and Default value. Name must be a String.
Value is traditionally a bool, but it can also be a float, int, or String. Qodot parses all these data types as Strings in the end, which will change how you will be Accessing Class Properties in Code.
The default value can be the previous data type, or even null. It is not read by Qodot, just the regular Value.